What is SSD SATA,Difference and Comparison | Xishuo
SSD SATA (Solid State Drive – Serial ATA) refers to a type of solid-state storage drive that connects to a computer via the SATA (Serial ATA) interface. SATA is an older interface typically used for connecting hard drives and optical drives to the motherboard. While SSDs can connect to a variety of interfaces, the term "SSD SATA" specifically indicates that the SSD uses the same interface as traditional spinning hard drives, but with flash memory inside.

Key Differences Between SSD SATA and Other SSD Types (e.g., NVMe)
Interface:
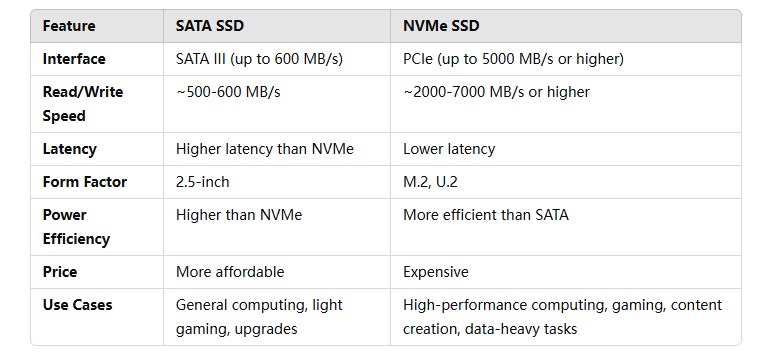
SATA SSD: Uses the SATA III interface, which is the same used for traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). The maximum data transfer rate of SATA III is around 600 MB/s.
NVMe SSD: Uses the PCIe interface (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), which offers significantly faster speeds—up to 5000 MB/s or higher for PCIe Gen 3. PCIe Gen 4 can offer even faster speeds.
Speed:
SATA SSD: Limited to the speed of the SATA interface, typically 500-600 MB/s sequential read/write speeds. Random read/write speeds can be lower.
NVMe SSD: Much faster, with sequential read/write speeds in the 2000-7000 MB/s range (depending on the generation of PCIe).
Latency:
SATA SSD: Higher latency compared to NVMe SSDs, though much lower than traditional HDDs.
NVMe SSD: Lower latency due to the more direct connection to the CPU via PCIe lanes.
Form Factor:
SATA SSD: Typically comes in the 2.5-inch form factor, similar to laptop hard drives, making it compatible with most devices that support SATA drives.
NVMe SSD: Often comes in the M.2 or U.2 form factor, which is much smaller and used in modern laptops and desktops. M.2 NVMe drives are also available in different lengths (e.g., 2280, 22110).
Cost:
SATA SSD: Less expensive due to the older interface and slower performance.
NVMe SSD: More expensive, though prices have been dropping as the technology matures.
Power Consumption:
SATA SSD: Slightly higher power consumption compared to NVMe drives, but still lower than HDDs.
NVMe SSD: Typically more power-efficient than SATA SSDs, especially in high-performance models.
Use Cases:
SATA SSD: Ideal for everyday use, such as upgrading a laptop or desktop from an HDD to an SSD for faster performance. It's suitable for general users, casual gaming, and office work.
NVMe SSD: Best suited for users who need top-tier performance, such as gamers, video editors, or professionals working with large files, and those who build high-performance desktops or workstations.
Performance Comparison
Conclusion:
SATA SSD is a good choice if you want to upgrade from an HDD or for general usage where extremely high speeds aren't necessary.
NVMe SSD is better suited for performance-intensive tasks such as gaming, video editing, and professional applications that require fast data transfer and low latency.
The key takeaway is that SATA SSDs are slower but more affordable, while NVMe SSDs offer much faster speeds at a higher cost.